Table of Contents
Path Analysis
Introduction
Regressions vs. Path Analysis (or SEM)
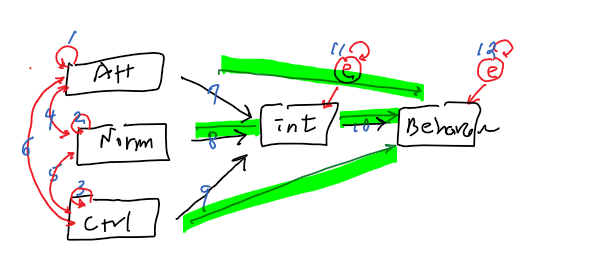
- Intention = a1 + b1(Attitude) + b2(Norms) + b3(Control)
- Behavior = a2 + b4(Intention)
- When in a combined situation, we use
- Path Analysis or SEM
Model Identification
- Terms
- The number of unique (non-redundent) source of information
- $p(p+1)/2$
- The number of parameters (paths) specified in model
- Just-identified (df = 0)
- Model can be estimated, but cannot be assessed
- Over-identified (df > 0)
- Model can be estimated and assessed
- Under-identified (df < 0)
- Model cannot be either estimated or assessed
- Exogenous and
- Endogenous Variables
- Covariance
- Variance
- Path coefficient
- Residual error
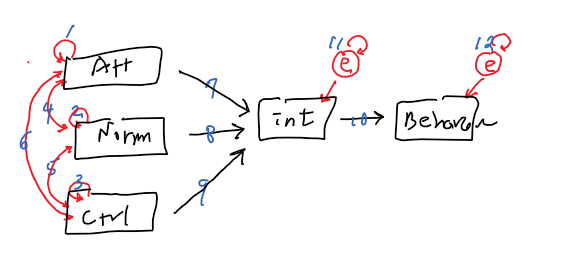
out of possible 15 relationships
15 - 12 =3 (df)
- Model fit
- Chi-square Test: p-value less than p-critical value (.05 for example) indicates that model does not fit well enough. p-value more than critical value means the model fits the data relatively well. The test is sensitive to the sample size and normality of the data.
- CFI (Comparative Fit Index): greater than .90 indicates good fit to the data. It is less sensitive to the sample size and normality of the data than chi-square test.
- TLI (Tucker-Lewis Index): greater than .95 (sometimes .90) indicates good fit. It is less sensitive to the sample size.
- RMSEA (Root Mean Square Error of Approximation): equal to or less than .08 (sometimes .10 is used) indicates good fit to the data.
- SRMR (Standard Root Mean square Residual): less than or equal to .08 indicates good fit to the data.
| $\chi^2$ | $\text{CFI}$ | $\text{TLI}$ | $\text{RMSEA}$ | $\text{SRMR}$ |
| $p \ge .05$ | $p \ge .90$ | $p \ge .95$ | $p \le .08$ | $p \le .08$ |
Then what is SEM (Structural Equation Modeling)
- Relationships within and among variables and constructs
E.g. in R
######################################################
## data file: PlannedBehavior.csv
######################################################
######################################################
install.packages("readr")
library(readr)
df <- read.csv("http://commres.net/wiki/_media/r/plannedbehavior.csv")
head(df)
str(df)
# path analysis in R using lavaan package
# install.packages("lavaan")
library(lavaan)
# Model speficiation
specmod <- "
intention ~ attitude + norms + control
"
# Estimate model
fitmod <- sem(specmod, data=df)
# summarize the result
summary(fitmod, fit.measures=TRUE, rsquare=TRUE)
specmod2
# Model speficiation 2
specmod2 <- "
intention ~ attitude + norms + control
attitude ~~ norms + control
norms ~~ control
"
fitmod2 <- sem(specmod2, data=df)
# summarize the result
summary(fitmod2, fit.measures=TRUE, rsquare=TRUE)
specmod3: lm
fitmod3 <- lm(intention~attitude+norms+control, data=df) summary(fitmod3)
specmod4
# pbt model
specmod4 <- "
# Directional relations (path)
intention ~ attitude + norms + control
behavior ~ intention
# Covariances
attitude ~~ norms + control
norms ~~ control
"
fitmod4 <- sem(specmod4, data=df)
summary(fitmod4, fit.measures=TRUE, rsquare=TRUE)
# my own
# pbt model
specmod5 <- '
# Directional relations (path)
intention ~ a*attitude + b*norms + c*control
behavior ~ d*intention
# Covariances
attitude ~~ norms + control
norms ~~ control
ad := a*d
bd := b*d
cd := c*d
'
fitmod5 <- sem(specmod5, data=df)
summary(fitmod5, fit.measures=TRUE, rsquare=TRUE)
Output
> df <- read.csv("http://commres.net/wiki/_media/r/plannedbehavior.csv")
> head(df)
attitude norms control intention behavior
1 2.31 2.31 2.03 2.50 2.62
2 4.66 4.01 3.63 3.99 3.64
3 3.85 3.56 4.20 4.35 3.83
4 4.24 2.25 2.84 1.51 2.25
5 2.91 3.31 2.40 1.45 2.00
6 2.99 2.51 2.95 2.59 2.20
> str(df)
'data.frame': 199 obs. of 5 variables:
$ attitude : num 2.31 4.66 3.85 4.24 2.91 2.99 3.96 3.01 4.77 3.67 ...
$ norms : num 2.31 4.01 3.56 2.25 3.31 2.51 4.65 2.98 3.09 3.63 ...
$ control : num 2.03 3.63 4.2 2.84 2.4 2.95 3.77 1.9 3.83 5 ...
$ intention: num 2.5 3.99 4.35 1.51 1.45 2.59 4.08 2.58 4.87 3.09 ...
$ behavior : num 2.62 3.64 3.83 2.25 2 2.2 4.41 4.15 4.35 3.95 ...
>
> # path analysis in R using lavaan package
> # install.packages("lavaan")
> library(lavaan)
This is lavaan 0.6-9
lavaan is FREE software! Please report any bugs.
Warning message:
패키지 ‘lavaan’는 R 버전 4.1.2에서 작성되었습니다
>
> # Model speficiation
> specmod <- "
+ intention ~ attitude + norms + control
+ "
> # Estimate model
> fitmod <- sem(specmod, data=df)
>
> # summarize the result
> summary(fitmod, fit.measures=TRUE, rsquare=TRUE)
lavaan 0.6-9 ended normally after 11 iterations
Estimator ML
Optimization method NLMINB
Number of model parameters 4
Number of observations 199
Model Test User Model:
Test statistic 0.000
Degrees of freedom 0
Model Test Baseline Model:
Test statistic 91.633
Degrees of freedom 3
P-value 0.000
User Model versus Baseline Model:
Comparative Fit Index (CFI) 1.000
Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) 1.000
Loglikelihood and Information Criteria:
Loglikelihood user model (H0) -219.244
Loglikelihood unrestricted model (H1) -219.244
Akaike (AIC) 446.489
Bayesian (BIC) 459.662
Sample-size adjusted Bayesian (BIC) 446.990
Root Mean Square Error of Approximation:
RMSEA 0.000
90 Percent confidence interval - lower 0.000
90 Percent confidence interval - upper 0.000
P-value RMSEA <= 0.05 NA
Standardized Root Mean Square Residual:
SRMR 0.000
Parameter Estimates:
Standard errors Standard
Information Expected
Information saturated (h1) model Structured
Regressions:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
intention ~
attitude 0.352 0.058 6.068 0.000
norms 0.153 0.059 2.577 0.010
control 0.275 0.058 4.740 0.000
Variances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
.intention 0.530 0.053 9.975 0.000
R-Square:
Estimate
intention 0.369
specmod2:
> # Model speficiation 2
> specmod2 <- "
+ intention ~ attitude + norms + control
+ attitude ~~ norms + control
+ norms ~~ control
+ "
> fitmod2 <- sem(specmod2, data=df)
>
> # summarize the result
> summary(fitmod2, fit.measures=TRUE, rsquare=TRUE)
lavaan 0.6-9 ended normally after 17 iterations
Estimator ML
Optimization method NLMINB
Number of model parameters 10
Number of observations 199
Model Test User Model:
Test statistic 0.000
Degrees of freedom 0
Model Test Baseline Model:
Test statistic 136.306
Degrees of freedom 6
P-value 0.000
User Model versus Baseline Model:
Comparative Fit Index (CFI) 1.000
Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) 1.000
Loglikelihood and Information Criteria:
Loglikelihood user model (H0) -1011.828
Loglikelihood unrestricted model (H1) -1011.828
Akaike (AIC) 2043.656
Bayesian (BIC) 2076.589
Sample-size adjusted Bayesian (BIC) 2044.908
Root Mean Square Error of Approximation:
RMSEA 0.000
90 Percent confidence interval - lower 0.000
90 Percent confidence interval - upper 0.000
P-value RMSEA <= 0.05 NA
Standardized Root Mean Square Residual:
SRMR 0.000
Parameter Estimates:
Standard errors Standard
Information Expected
Information saturated (h1) model Structured
Regressions:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
intention ~
attitude 0.352 0.058 6.068 0.000
norms 0.153 0.059 2.577 0.010
control 0.275 0.058 4.740 0.000
Covariances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
attitude ~~
norms 0.200 0.064 3.128 0.002
control 0.334 0.070 4.748 0.000
norms ~~
control 0.220 0.065 3.411 0.001
Variances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
.intention 0.530 0.053 9.975 0.000
attitude 0.928 0.093 9.975 0.000
norms 0.830 0.083 9.975 0.000
control 0.939 0.094 9.975 0.000
R-Square:
Estimate
intention 0.369
specmod3: lm
> fitmod3 <- lm(intention~attitude+norms+control, data=df)
> summary(fitmod3)
Call:
lm(formula = intention ~ attitude + norms + control, data = df)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-1.80282 -0.52734 -0.06018 0.51228 1.85202
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 0.58579 0.23963 2.445 0.0154 *
attitude 0.35232 0.05866 6.006 9.13e-09 ***
norms 0.15250 0.05979 2.550 0.0115 *
control 0.27502 0.05862 4.692 5.09e-06 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 0.7356 on 195 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.369, Adjusted R-squared: 0.3593
F-statistic: 38.01 on 3 and 195 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16
specmod4
>
> # pbt model
> specmod4 <- "
+ # Directional relations (path)
+ intention ~ attitude + norms + control
+ behavior ~ intention
+ # Covariances
+ attitude ~~ norms + control
+ norms ~~ control
+ "
> fitmod4 <- sem(specmod4, data=df)
> summary(fitmod4, fit.measures=TRUE, rsquare=TRUE)
lavaan 0.6-9 ended normally after 17 iterations
Estimator ML
Optimization method NLMINB
Number of model parameters 12
Number of observations 199
# chi-square test
# p-value is over .05 indicating . . . .
Model Test User Model:
Test statistic 2.023
Degrees of freedom 3
P-value (Chi-square) 0.568
Model Test Baseline Model:
Test statistic 182.295
Degrees of freedom 10
P-value 0.000
# CFI >_ .90
# TLI >_ .95
# The two indicate that the model fits to the data well
User Model versus Baseline Model:
Comparative Fit Index (CFI) 1.000
Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) 1.019
Loglikelihood and Information Criteria:
Loglikelihood user model (H0) -1258.517
Loglikelihood unrestricted model (H1) -1257.506
Akaike (AIC) 2541.035
Bayesian (BIC) 2580.555
Sample-size adjusted Bayesian (BIC) 2542.538
# RMSEA <_ .08
#
Root Mean Square Error of Approximation:
RMSEA 0.000
90 Percent confidence interval - lower 0.000
90 Percent confidence interval - upper 0.103
P-value RMSEA <= 0.05 0.735
# SRMR <_ .08 meets the standard
#
Standardized Root Mean Square Residual:
SRMR 0.019
Parameter Estimates:
Standard errors Standard
Information Expected
Information saturated (h1) model Structured
Regressions:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
intention ~
attitude 0.352 0.058 6.068 0.000
norms 0.153 0.059 2.577 0.010
control 0.275 0.058 4.740 0.000
behavior ~
intention 0.453 0.065 7.014 0.000
Covariances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
attitude ~~
norms 0.200 0.064 3.128 0.002
control 0.334 0.070 4.748 0.000
norms ~~
control 0.220 0.065 3.411 0.001
Variances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
.intention 0.530 0.053 9.975 0.000
.behavior 0.699 0.070 9.975 0.000
attitude 0.928 0.093 9.975 0.000
norms 0.830 0.083 9.975 0.000
control 0.939 0.094 9.975 0.000
R-Square:
Estimate
intention 0.369
behavior 0.198
specmod5
> specmod5 <- "
+ # Directional relations (path)
+ intention ~ attitude + norms + control
+ behavior ~ intention + norms
+ # Covariances
+ attitude ~~ norms + control
+ norms ~~ control
+ "
> fitmod5 <- sem(specmod5, data=df)
> summary(fitmod5, fit.measures=TRUE, rsquare=TRUE)
lavaan 0.6-12 ended normally after 18 iterations
Estimator ML
Optimization method NLMINB
Number of model parameters 13
Number of observations 199
Model Test User Model:
Test statistic 1.781
Degrees of freedom 2
P-value (Chi-square) 0.410
Model Test Baseline Model:
Test statistic 182.295
Degrees of freedom 10
P-value 0.000
User Model versus Baseline Model:
Comparative Fit Index (CFI) 1.000
Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) 1.006
Loglikelihood and Information Criteria:
Loglikelihood user model (H0) -1258.396
Loglikelihood unrestricted model (H1) -1257.506
Akaike (AIC) 2542.792
Bayesian (BIC) 2585.605
Sample-size adjusted Bayesian (BIC) 2544.421
Root Mean Square Error of Approximation:
RMSEA 0.000
90 Percent confidence interval - lower 0.000
90 Percent confidence interval - upper 0.136
P-value RMSEA <= 0.05 0.569
Standardized Root Mean Square Residual:
SRMR 0.018
Parameter Estimates:
Standard errors Standard
Information Expected
Information saturated (h1) model Structured
Regressions:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
intention ~
attitude 0.352 0.058 6.068 0.000
norms 0.153 0.059 2.577 0.010
control 0.275 0.058 4.740 0.000
behavior ~
intention 0.443 0.068 6.525 0.000
norms 0.034 0.068 0.493 0.622
Covariances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
attitude ~~
norms 0.200 0.064 3.128 0.002
control 0.334 0.070 4.748 0.000
norms ~~
control 0.220 0.065 3.411 0.001
Variances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
.intention 0.530 0.053 9.975 0.000
.behavior 0.698 0.070 9.975 0.000
attitude 0.928 0.093 9.975 0.000
norms 0.830 0.083 9.975 0.000
control 0.939 0.094 9.975 0.000
R-Square:
Estimate
intention 0.369
behavior 0.199
Lavaan in R: explanation
Path analysis in R with Lavaan (introduction)
By Mike Crowson, Ph.D.
September 17, 2019
- Overview: There are two basic functions that allow you to run path analysis in Lavaan: the 'sem' and the 'lavaan' functions.This video will demonstrate how to specify a path model involving only manifest variables and how to estimate model parameters using the 'lavaan' function. A copy of this text file and a .csv file containing the raw data will be available for download underneath the video description. You will notice that I use the pound sign (#) in some of the syntax. The # sign is used for comments and are not read by the program. I use it in some of the syntax below to provide annotations.
- If you have not already done so, you will need to install Lavaan.
install.packages("lavaan")
- Read data into R and store in data object. Make sure you have R correctly pointed to the folder containing your data. Below is syntax to create a data frame called 'processdata' when reading the .csv file (referenced above) into R.This is the data frame we will be using when running our analyses.
# processdata<-read.csv("path analysis dataN BinW.csv", header=TRUE, sep=",")
processdata<-read.csv("http://commres.net/wiki/_media/r/path_analysis_datan_binw.csv",
header=TRUE, sep=",", fileEncoding="UTF-8-BOM")
- Using the 'str' function, you can look at the structure of the data.
str(processdata)
- Use libary function to call up lavaan
library(lavaan)
- 'lavaan' function
- Step 1: Use lavaan model syntax to specify path model and have it stored in an R object. In our model, we will treat ses, mastery goals, and performance goals as predictors of student achievement. The effect of mastery on achievement will be both direct and indirect (via interest and anxiety. The effects of ses and performance goals will be treated as being fully mediated through anxiety and interest.
- When specifying predictive relationships in the model, we use the tilde sign ('~'), which separates thedependent variable in each equation from its predictors. Predictors are separated in each equation by '+' sign. In our model, we will also allow the residuals for anxiety and interest to correlate (see '~~' in syntax below)
# model specification model <- ' #equation where interest is predicted by ses # & mastery and performance goals interest ~ mastery + perfgoal + ses # equation where achieve is predicted by # interest and anxiety achieve ~ anxiety + interest + mastery # equation where anxiety is predicted # by mastery and performance goals anxiety ~ perfgoal + mastery # estimating the variances of # the exogenous variables (ses, mastery,performance) mastery ~~ mastery perfgoal ~~ perfgoal ses ~~ ses # estimtating the covariances of the exogenous # variables (ses, mastery,performance) mastery ~~ perfgoal + ses perfgoal ~~ ses # estimating the residual variances # for endogenous variables (interest, anxiety, achieve) interest ~~ interest anxiety ~~ anxiety achieve ~~ achieve # estimating the covariance of residuals # for interest and anxiety interest ~~ anxiety '
- Step 2: Use 'lavaan' function to run analysis. Here, I will be saving the results in an R object called 'fit' (arbitrarily named). Inside the parenthesis are arguments separated by commas. The first argument contains the name of the object containing the model syntax (see above). The object is named 'model' (again, arbitrarily named above). Next, we have the 'data' argument. This identifies the object (i.e., data frame) containing the raw data.
fit<-lavaan(model, data=processdata)
- The 'summary' function can be used to obtain various fit measures and the parameter estimates for the model
summary(fit, fit.measures=TRUE)
- To obtain standardized estimates, use the 'standardized' argument (setting it to TRUE) when using the 'summary' function. You will need to interpret the Std.all column in the output, as it will provide standardized estimates for all measured variables in the model.
summary(fit, fit.measures=TRUE, standardized=TRUE, rsquare=TRUE)
- Using the 'parameterEstimates' function, you can obtain confidence intervals
parameterEstimates(fit)
- For a more comprehensive set of fit measures, use the 'fitMeasures' function
fitMeasures(fit)
- To obtain modification indices, you can use the 'modificationIndices' function
modificationIndices(fit)
- Note: Modification indices represent the expected decrease in model chi-square after freeing a given parameter (Schumacker & Lomax, 2004). The EPC is an estimate of the model parameter itself. A MI value of 3.84 or greater may be considered “significant” (at the .05) level. Warning: This is totally an empirically based approach to model specification. Consult your theory when using these!
output
> # install.packages("lavaan")
>
> # processdata<-read.csv("path analysis dataN BinW.csv", header=TRUE, sep=",")
> processdata<-read.csv("http://commres.net/wiki/_media/r/path_analysis_datan_binw.csv",
+ header=TRUE, sep=",", fileEncoding="UTF-8-BOM")
>
> str(processdata)
'data.frame': 140 obs. of 9 variables:
$ id : int 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ...
$ ses : int 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 ...
$ genderid: int 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 ...
$ perfgoal: num 29.5 29.5 30.4 33.5 28.7 ...
$ achieve : num 6.12 1.62 4.5 2.38 5.12 ...
$ mastery : num 5.71 1.43 1.29 2.29 4.57 ...
$ interest: num 6 4 2 4 5.5 4 4 5 4.5 4 ...
$ anxiety : num 1.67 6.33 3.67 3.67 3.67 ...
$ pgoal_MS: int 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 ...
> library(lavaan)
>
> # model specification
> model <- '
+ # equation where interest is predicted by ses
+ # & mastery and performance goals
+ interest ~ mastery + perfgoal + ses
+
+ # equation where achieve is predicted by
+ # interest and anxiety
+ achieve ~ anxiety + interest + mastery
+
+ # equation where anxiety is predicted
+ # by mastery and performance goals
+ anxiety ~ perfgoal + mastery
+
+ # estimating the variances of
+ # the exogenous variables (ses, mastery,performance)
+ mastery ~~ mastery
+ perfgoal ~~ perfgoal
+ ses ~~ ses
+
+ # estimtating the covariances of the exogenous
+ # variables (ses, mastery,performance)
+ mastery ~~ perfgoal + ses
+ perfgoal ~~ ses
+
+ # estimating the residual variances
+ # for endogenous variables (interest, anxiety, achieve)
+ interest ~~ interest
+ anxiety ~~ anxiety
+ achieve ~~ achieve
+
+ # estimating the covariance of residuals
+ # for interest and anxiety
+ interest ~~ anxiety '
>
> fit<-lavaan(model, data=processdata)
> summary(fit, fit.measures=TRUE)
lavaan 0.6.16 ended normally after 27 iterations
Estimator ML
Optimization method NLMINB
Number of model parameters 18
Number of observations 140
Model Test User Model:
Test statistic 29.231
Degrees of freedom 3
P-value (Chi-square) 0.000
Model Test Baseline Model:
Test statistic 202.409
Degrees of freedom 15
P-value 0.000
User Model versus Baseline Model:
Comparative Fit Index (CFI) 0.860
Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) 0.300
Loglikelihood and Information Criteria:
Loglikelihood user model (H0) -1391.274
Loglikelihood unrestricted model (H1) -1376.659
Akaike (AIC) 2818.548
Bayesian (BIC) 2871.498
Sample-size adjusted Bayesian (SABIC) 2814.548
Root Mean Square Error of Approximation:
RMSEA 0.250
90 Percent confidence interval - lower 0.172
90 Percent confidence interval - upper 0.336
P-value H_0: RMSEA <= 0.050 0.000
P-value H_0: RMSEA >= 0.080 1.000
Standardized Root Mean Square Residual:
SRMR 0.074
Parameter Estimates:
Standard errors Standard
Information Expected
Information saturated (h1) model Structured
Regressions:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
interest ~
mastery 0.708 0.088 8.066 0.000
perfgoal -0.035 0.040 -0.879 0.380
ses 0.520 0.242 2.154 0.031
achieve ~
anxiety -0.040 0.054 -0.747 0.455
interest 0.211 0.060 3.527 0.000
mastery 0.345 0.079 4.358 0.000
anxiety ~
perfgoal 0.025 0.045 0.556 0.578
mastery -0.387 0.097 -4.009 0.000
Covariances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
mastery ~~
perfgoal -0.935 0.361 -2.590 0.010
ses 0.170 0.061 2.805 0.005
perfgoal ~~
ses -0.226 0.128 -1.768 0.077
.interest ~~
.anxiety 0.059 0.181 0.329 0.742
Variances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|)
mastery 1.944 0.232 8.367 0.000
perfgoal 8.936 1.068 8.367 0.000
ses 0.249 0.030 8.367 0.000
.interest 1.895 0.227 8.367 0.000
.anxiety 2.410 0.288 8.367 0.000
.achieve 0.988 0.118 8.367 0.000
> summary(fit, fit.measures=TRUE, standardized=TRUE, rsquare=TRUE)
lavaan 0.6.16 ended normally after 27 iterations
Estimator ML
Optimization method NLMINB
Number of model parameters 18
Number of observations 140
Model Test User Model:
Test statistic 29.231
Degrees of freedom 3
P-value (Chi-square) 0.000
Model Test Baseline Model:
Test statistic 202.409
Degrees of freedom 15
P-value 0.000
User Model versus Baseline Model:
Comparative Fit Index (CFI) 0.860
Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) 0.300
Loglikelihood and Information Criteria:
Loglikelihood user model (H0) -1391.274
Loglikelihood unrestricted model (H1) -1376.659
Akaike (AIC) 2818.548
Bayesian (BIC) 2871.498
Sample-size adjusted Bayesian (SABIC) 2814.548
Root Mean Square Error of Approximation:
RMSEA 0.250
90 Percent confidence interval - lower 0.172
90 Percent confidence interval - upper 0.336
P-value H_0: RMSEA <= 0.050 0.000
P-value H_0: RMSEA >= 0.080 1.000
Standardized Root Mean Square Residual:
SRMR 0.074
Parameter Estimates:
Standard errors Standard
Information Expected
Information saturated (h1) model Structured
Regressions:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|) Std.lv Std.all
interest ~
mastery 0.708 0.088 8.066 0.000 0.708 0.558
perfgoal -0.035 0.040 -0.879 0.380 -0.035 -0.060
ses 0.520 0.242 2.154 0.031 0.520 0.147
achieve ~
anxiety -0.040 0.054 -0.747 0.455 -0.040 -0.053
interest 0.211 0.060 3.527 0.000 0.211 0.294
mastery 0.345 0.079 4.358 0.000 0.345 0.379
anxiety ~
perfgoal 0.025 0.045 0.556 0.578 0.025 0.045
mastery -0.387 0.097 -4.009 0.000 -0.387 -0.327
Covariances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|) Std.lv Std.all
mastery ~~
perfgoal -0.935 0.361 -2.590 0.010 -0.935 -0.224
ses 0.170 0.061 2.805 0.005 0.170 0.244
perfgoal ~~
ses -0.226 0.128 -1.768 0.077 -0.226 -0.151
.interest ~~
.anxiety 0.059 0.181 0.329 0.742 0.059 0.028
Variances:
Estimate Std.Err z-value P(>|z|) Std.lv Std.all
mastery 1.944 0.232 8.367 0.000 1.944 1.000
perfgoal 8.936 1.068 8.367 0.000 8.936 1.000
ses 0.249 0.030 8.367 0.000 0.249 1.000
.interest 1.895 0.227 8.367 0.000 1.895 0.606
.anxiety 2.410 0.288 8.367 0.000 2.410 0.884
.achieve 0.988 0.118 8.367 0.000 0.988 0.613
R-Square:
Estimate
interest 0.394
anxiety 0.116
achieve 0.387
>
> parameterEstimates(fit)
lhs op rhs est se z pvalue ci.lower ci.upper
1 interest ~ mastery 0.708 0.088 8.066 0.000 0.536 0.880
2 interest ~ perfgoal -0.035 0.040 -0.879 0.380 -0.114 0.043
3 interest ~ ses 0.520 0.242 2.154 0.031 0.047 0.994
4 achieve ~ anxiety -0.040 0.054 -0.747 0.455 -0.146 0.066
5 achieve ~ interest 0.211 0.060 3.527 0.000 0.094 0.328
6 achieve ~ mastery 0.345 0.079 4.358 0.000 0.190 0.500
7 anxiety ~ perfgoal 0.025 0.045 0.556 0.578 -0.063 0.113
8 anxiety ~ mastery -0.387 0.097 -4.009 0.000 -0.576 -0.198
9 mastery ~~ mastery 1.944 0.232 8.367 0.000 1.488 2.399
10 perfgoal ~~ perfgoal 8.936 1.068 8.367 0.000 6.842 11.029
11 ses ~~ ses 0.249 0.030 8.367 0.000 0.191 0.308
12 mastery ~~ perfgoal -0.935 0.361 -2.590 0.010 -1.642 -0.227
13 mastery ~~ ses 0.170 0.061 2.805 0.005 0.051 0.288
14 perfgoal ~~ ses -0.226 0.128 -1.768 0.077 -0.476 0.024
15 interest ~~ interest 1.895 0.227 8.367 0.000 1.451 2.339
16 anxiety ~~ anxiety 2.410 0.288 8.367 0.000 1.845 2.974
17 achieve ~~ achieve 0.988 0.118 8.367 0.000 0.757 1.220
18 interest ~~ anxiety 0.059 0.181 0.329 0.742 -0.295 0.414
> fitMeasures(fit)
npar fmin chisq
18.000 0.104 29.231
df pvalue baseline.chisq
3.000 0.000 202.409
baseline.df baseline.pvalue cfi
15.000 0.000 0.860
tli nnfi rfi
0.300 0.300 0.278
nfi pnfi ifi
0.856 0.171 0.868
rni logl unrestricted.logl
0.860 -1391.274 -1376.659
aic bic ntotal
2818.548 2871.498 140.000
bic2 rmsea rmsea.ci.lower
2814.548 0.250 0.172
rmsea.ci.upper rmsea.ci.level rmsea.pvalue
0.336 0.900 0.000
rmsea.close.h0 rmsea.notclose.pvalue rmsea.notclose.h0
0.050 1.000 0.080
rmr rmr_nomean srmr
0.122 0.122 0.074
srmr_bentler srmr_bentler_nomean crmr
0.074 0.074 0.088
crmr_nomean srmr_mplus srmr_mplus_nomean
0.088 0.074 0.074
cn_05 cn_01 gfi
38.428 55.335 0.941
agfi pgfi mfi
0.587 0.134 0.911
ecvi
0.466
> modificationIndices(fit)
lhs op rhs mi epc sepc.lv sepc.all sepc.nox
19 interest ~~ achieve 25.396 -2.899 -2.899 -2.118 -2.118
23 achieve ~~ anxiety 6.669 6.803 6.803 4.408 4.408
24 achieve ~~ mastery 22.476 -1.743 -1.743 -1.257 -1.257
25 achieve ~~ perfgoal 2.763 -0.406 -0.406 -0.137 -0.137
26 achieve ~~ ses 20.541 0.186 0.186 0.376 0.376
27 anxiety ~~ mastery 0.921 0.765 0.765 0.354 0.354
28 anxiety ~~ perfgoal 0.921 -3.576 -3.576 -0.771 -0.771
29 anxiety ~~ ses 0.921 -0.061 -0.061 -0.078 -0.078
30 interest ~ achieve 25.396 -2.933 -2.933 -2.106 -2.106
32 achieve ~ perfgoal 4.551 -0.062 -0.062 -0.146 -0.146
33 achieve ~ ses 22.431 0.837 0.837 0.329 0.329
34 anxiety ~ interest 0.921 -0.502 -0.502 -0.538 -0.538
35 anxiety ~ achieve 1.119 1.922 1.922 1.478 1.478
36 anxiety ~ ses 0.921 -0.261 -0.261 -0.079 -0.079
37 mastery ~ interest 0.923 12.889 12.889 16.348 16.348
38 mastery ~ achieve 22.801 -1.774 -1.774 -1.616 -1.616
39 mastery ~ anxiety 0.921 0.318 0.318 0.376 0.376
43 perfgoal ~ achieve 2.745 -0.410 -0.410 -0.174 -0.174
44 perfgoal ~ anxiety 0.921 -1.484 -1.484 -0.820 -0.820
47 ses ~ interest 0.923 -1.021 -1.021 -3.618 -3.618
48 ses ~ achieve 20.964 0.190 0.190 0.484 0.484
49 ses ~ anxiety 0.921 -0.025 -0.025 -0.083 -0.083
>
>
- Specification of model using auto.var argument…
# model specification model<-' # equation where interest is predicted by ses & mastery and # performance goals interest ~ mastery + perfgoal + ses # equation where achieve is predicted by interest and anxiety achieve~anxiety+interest+mastery #equation where anxiety is predicted by mastery and performance goals anxiety~perfgoal+mastery # estimtating the variances of the exogenous variables (ses, mastery,performance) mastery~~mastery perfgoal~~perfgoal ses~~ses # estimtating the covariances of the exogenous variables (ses, mastery,performance) mastery~~perfgoal+ses perfgoal~~ses # The auto.var argument when fitting the model can be used so that # you do not have to directly request estimation of residual variances # Estimating the covariance of residuals for interest and anxiety interest~~anxiety' fit<-lavaan(model, data=processdata, auto.var=TRUE) summary(fit, fit.measures=TRUE, standardized=TRUE, rsquare=TRUE)
- There are a couple of ways you can obtain path diagrams (although they can be somewhat tricky to implement.
- One approach is to use the 'semPaths' function from the 'semPlot' package. Below, I provide a rough demo of this approach. Citations containing additional information is provided below the demo.
install.packages("semPlot")
library("semPlot")
semPaths(fit,what="paths",whatLabels="par",style="lisrel",layout="tree",
rotation=2)
- A second approach is to use the 'lavaanPlot“ function from the 'lavaanPlot' package.
install.packages("lavaanPlot")
library(lavaanPlot)
lavaanPlot(model = fit,
node_options = list(shape = "box", fontname = "Helvetica"),
edge_options = list(color = "grey"),
coefs = TRUE,
covs = TRUE,
stars = c("regress"))
Resources on the use of lavaan:
Using the 'semPlot' package
Using the 'lavaanPlot' package
Raw data for all examples can be downloaded at…
A copy of the Powerpoint of the model specification can be downloaded at…
Basics of path analysis using Lavaan.txt
Displaying Basics of path analysis using Lavaan.txt.
CODING
processdata<-read.csv("http://commres.net/wiki/_media/r/path_analysis_datan_binw.csv",
header=TRUE, sep=",", fileEncoding="UTF-8-BOM")
str(processdata)
library(lavaan)
model <- '
interest ~ mastery + perfgoal + ses
achieve ~ anxiety + interest + mastery
anxiety ~ perfgoal + mastery
# variances
mastery ~~ mastery
perfgoal ~~ perfgoal
ses ~~ ses
mastery ~~ perfgoal + ses
perfgoal ~~ ses
interest ~~ interest
anxiety ~~ anxiety
achieve ~~ achieve
interest~~anxiety
'
fit <- lavaan(model, data=processdata)
fit <- sem(model, data=processdata)
summary(fit, fit.measures=TRUE)
summary(fit, fit.measures=TRUE, standardized=TRUE, rsquare=TRUE)
parameterEstimates(fit)
fitMeasures(fit)
modificationIndices(fit)
install.packages("semPlot")
library("semPlot")
semPaths(fit,what="paths",whatLabels="par",style="lisrel",layout="tree",
rotation=2)
install.packages("lavaanPlot")
library(lavaanPlot)
lavaanPlot(
model = fit,
node_options = list(shape = "box", fontname = "Helvetica"),
edge_options = list(color = "grey"),
coefs = TRUE, covs=TRUE,
stars = c("regress"))
Lavaan 2
model <- '
# labeling path from mastery to interest
interest ~ a*mastery + perfgoal + ses
# labeling path from interest to achieve.
# Adding labeled path from
# mastery to achieve
achieve ~ e*anxiety + b*interest + c*mastery
# predicting anxiety and labeling path from mastery
anxiety ~ perfgoal + d*mastery
# estimtating the variances and covariances of
# the exogenous variables (ses, mastery,performance)
mastery~~mastery
perfgoal~~perfgoal
ses~~ses
mastery~~perfgoal+ses
perfgoal~~ses
# estimating the variances of residuals
# for endogenous variables
# (interest, anxiety, achieve)
interest~~interest
anxiety~~anxiety
achieve~~achieve
# estimating the covariance of residuals
# for interest and anxiety
interest~~anxiety
# calculating specific indirect effect
# of mastery on achieve via interest
SIE1:=a*b
# calculating specific indirect effect of
# mastery on achieve via anxiety
SIE2:=d*e
# calculating total indirect effect of
# mastery on achievement via mediators
TIE:=SIE1+SIE2
# calculating total effect of mastery on achieve
TE:=TIE+c'
# using naive bootstrap to obtain standard errors
fit <- sem(model, data=processdata, se="bootstrap")
summary(fit,fit.measures=TRUE)
# using 'parameterEstimates' function will give
# us confidence intervals based on naive bootstrap.
# A standard approach to testing indirect effects.
parameterEstimates(fit)
Lavaan 3: Testing data normality
processdata <- read.csv("http://commres.net/wiki/_media/r/path_analysis_datan_binw.csv")
str(processdata)
# install.packages("MVN")
library(MVN)
newdata <- processdata[c("achieve", "interest", "anxiety")]
str(newdata)
Use the 'mvn' function to evalue normality
Multivariate normality is evidenced by p-values associated with multivariate skewness and kurtosis statistics that are > .05. In those cases where both the skewness and kurtosis results are non-significant (p's > .05), then the data are assumed to follow a multivariate normal distribution where p > .05 (Korkmaz, Goksuluk, & Zarasiz, 2014, 2019).
You can also use plots to explore possible multivariate outliers. Moreover, you can examine univariate tests of normality (the default is Shapiro-Wilk test, but can be changed if desired). A significant test result regarding a specific variable indicates a significant departure from normality.
mvn(newdata, mvnTest="mardia") mvn(newdata, multivariatePlot="qq") mvn(newdata, multivariateOutlierMethod="quan")
You can generate univariate plot as well to evaluate distribution of the endogenous variables for non-normality. Skewness values approaching 2 or kurtoisis values over 7 may be considered indicative of more “significant problems” with non-normality (Curran, et al., 1996).
mvn(newdata, univariatePlot="histogram")
mvn(newdata, univariatePlot="box")
model <- '
interest ~ mastery + perfgoal + ses
achieve ~ anxiety + interest + mastery
anxiety ~ perfgoal + mastery
# variances
mastery ~~ mastery
perfgoal ~~ perfgoal
ses ~~ ses
mastery ~~ perfgoal + ses
perfgoal ~~ ses
interest ~~ interest
anxiety ~~ anxiety
achieve ~~ achieve
interest~~anxiety
'
We will fit the model using the 'estimator' argument at set it equal to “MLM.” This will result in the Satorra-Bentler model chi-square being computed. We will also use the 'se' argument and set it to “roburst.”
fit <- sem(model, data=processdata, estimator = "MLM", se="roburst") summary(fit,fit.measures=TRUE)
reference
see lme4 tutorial
Exercise
Using mtcars in R
?mtcars mtcars str(mtcars) df <- mtcars
# model specfication model <-' mpg ~ hp + gear + cyl + disp + carb + am + wt hp ~ cyl + disp + carb ' # model fit fit <- cfa(model, data = mtcars) summary(fit, fit.measures = TRUE, standardized=T, rsquare=T) semPaths(fit, 'std', layout = 'circle')