About Big Data
Usually defined by three elements:
- Volume
- Velocity (speed)
- Variety
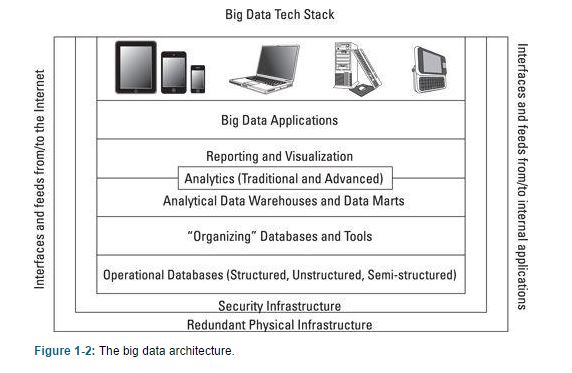
Proper organization and use of them is as much important as having them.
Organizations
- Relational Data Model: RDBMS (Relational Database Management System), mainly implemently by SQL (Structured Query Language).
- Entity-Relationship Data Model (ER): . . . It added additional abstraction to increase the usability of the data. In the model, each item was defined independently of its use. Therefore, developers could create new relationships between data sources without complex programming 1).
- Data warehouse in 90s
- Beginning of unstructured data use – BLOBs (Binary Large Objects)
- Object Database Management System (ODBMS).
The above has shown Structured → Unstructured data. Therefore, building, organizing, integrating, analyzing, and deciding (utilizing the data) become extremely important.
- COIAA – Capture, Organize, Integrate, Analyze, Act
Capture
- Setting architectural foundation
Sources of big structured data
- Computer-generated or Machine-generated Data
- Human-generated Data
- Computer-generated or Machine-generated Data
- Sensor data . . . . RFID tags, Smart meters, medical devices, GPS data, etc.
- Web log data . . . Google analytics,
- Point-of-sale data . . . Cashiers' swipes . . . .
- Financial data
- Human-generated Data
- Input data . . . .
- Click stream data . . . .
- Gaming-related data . . . .
Sources of unstructured data
Exploring sources of unstructured data
Unstructured data is everywhere. In fact, most individuals and organizations conduct their lives around unstructured data. Just as with structured data, unstructured data is either machine generated or human generated.
Here are some examples of machine-generated unstructured data:
- Satellite images: This includes weather data or the data that the government captures in its satellite surveillance imagery. Just think about Google Earth, and you get the picture (pun intended).
- Scientific data: This includes seismic imagery, atmospheric data, and high energy physics.
- Photographs and video: This includes security, surveillance, and traffic video.
- Radar or sonar data: This includes vehicular, meteorological, and oceanographic seismic profiles.
The following list shows a few examples of human-generated unstructured data:
- Text internal to your company: Think of all the text within documents, logs, survey results, and e-mails. Enterprise information actually represents a large percent of the text information in the world today.
- Social media data: This data is generated from the social media platforms such as YouTube, Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and Flickr.
- Mobile data: This includes data such as text messages and location information.
- Website content: This comes from any site delivering unstructured content, like YouTube, Flickr, or Instagram.