Table of Contents
Week01 (Sep. 4, 7)
1. Introduction
2. Descriptive Statistics
3. Standard Score
4. Intro to hypothesis testing
5. Sampling
6. HT with one sample
7. Selecting samples for comparison
8. HT with two samples
9. Significance, error and power
10. Intro to the analysis of variance
11. One factor independent measure ANOVA
12. Multiple comparisons
13. One factor repeated measure ANOVA
14. Interaction of factors in the ANOVA
15. Calculating two factor ANOVA
16.
17.
18. One factor ANOVA for ranked data
19. Chi-square
20. Linear correlation and regression
21. Multiple correlation and regression
22. Complex analyses and computers
23. An introduction to the general linear model
ideas and concepts
Introduction to R and others
- Downloading and Installing R
- Starting R
- Entering Commands
- Exiting from R
- Interrupting R
- Viewing the Supplied Documentation
- Getting Help on a Function
- Searching the Supplied Documentation
- Getting Help on a Package
- Searching the Web for Help
- Finding Relevant Functions and Packages
- Searching the Mailing Lists
- Submitting Questions to the Mailing Lists
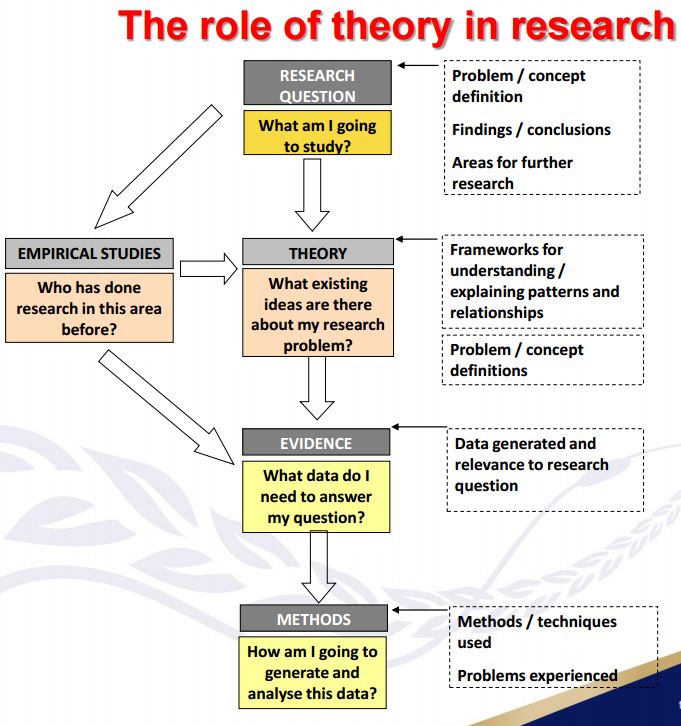
using theories and making hypotheses
Assignment
Week02 (Sep. 11, 14)
Concepts and ideas
Some basics
- Introduction
- Printing Something
- Setting Variables
- Listing Variables
- Deleting Variables
- Creating a Vector
- Computing Basic Statistics
- Creating Sequences
- Comparing Vectors
- Selecting Vector Elements
- Performing Vector Arithmetic
- Getting Operator Precedence Right
- Defining a Function
- Typing Less and Accomplishing More
- Avoiding Some Common Mistakes
Chater 2. Descriptive Statistics
- Measures of 'central tendency'
- Measures of 'spread'
- Describing a set of data: in conclusion
- Comparing two sets of data with descriptive statistics
- Some important information about numbers
—-
using theories and making hypotheses
- Theories
- to build science
- to guide as a frame (what to look, how to think, and how to look at)
- to explain phenomena
- to predict phenomena (to provide a context for predictions)
- Empirically relevant (testing) and always tentative (deductive cycle)
- via research (hypothesis testing)
- hence, not fixed
- generalized statement regarding a connection between A and B (idea, concept, construct, phenomena, etc)
- Levels ?
- Micro . . . frustration and aggression
- Meso . . . online communities and disinhibition
- Macro . . . ethnicity (or socio-econ class) and family bond
- role of T
- Research Questions (or Problems)
- Two ideas guided by theories
- Questions on their relationships
- Conceptualization
-
- Educated guess (via theories)
- Difference
- Association
- Variables (vs. ideas, concepts, and constructs)
-
- Control variable
- Mediating (Intervening) variable
Assignment
Week03 (Sep. 18, 21)
Concepts and ideas
Navigating software
- Introduction
- Getting and Setting the Working Directory
- Saving Your Workspace
- Viewing Your Command History
- Saving the Result of the Previous Command
- Displaying the Search Path
- Accessing the Functions in a Package
- Accessing Built-in Datasets
- Viewing the List of Installed Packages
- Installing Packages from CRAN
- Setting a Default CRAN Mirror
- Suppressing the Startup Message
- Running a Script
- Running a Batch Script
- Getting and Setting Environment Variables
- Locating the R Home Directory
- Customizing R
Mean
Mode
Median
Variance
Standard Deviation
+-1 sd = 68% = +-1 sd
+-2 sd = 95% = +-1.96 sd
+-3 sd = 99% (99.7%) = +-3 sd
표준점수 (unit with a standard deviation) = z score
Sampling distribution via random sampling
Central Limit Theorem
Hypothesis testing
z-test
Assignment
Find two research articles that have listed hypotheses (social science research article would be good option). For each article:
- 각 가설을 적고
- 독립변인과 종속변인 그리고 intervening (moderator) 변인 등이 무엇인지 설명하시오.
- 각 변인이 어떻게 측정되었는지 설명하시오.
- 각 가설이 어떤 종류인지 설명하시오. (차이, 연관의 가설)
- 가설검증을 위해서 어떤 테스트방법을 취했는지 찾아서 기록하시오.
due date: 다음 주 수요일 자정까지 완성하시오 (2018/09/26 11:59).
Week04 (Sep. 25, 28)
Sep. 25: Harvest Evening (23, 24, 25, 26)
Class Activity
- 가설 만들어 보기
- how to write hypothesis at behavioral science writing.
- One sample hypothesis Hypothesis at www.socialresearchmethods.net
- r 에서 qnorm(proportion) pnorm(z-score) function 이해 필요
- z_score 참조
- r 에서, qt(proportion, df), pt(t-score, df) function 이해 필요
- probability 참조
Concepts and ideas
- Introduction
- Entering Data from the Keyboard
- Printing Fewer Digits (or More Digits)
- Redirecting Output to a File
- Listing Files
- Dealing with “Cannot Open File” in Windows
- Reading Fixed-Width Records
- Reading Tabular Data Files
- Reading from CSV Files
- Writing to CSV Files
- Reading Tabular or CSV Data from the Web
- Reading Data from HTML Tables
- Reading Files with a Complex Structure
- Reading from MySQL Databases
- Saving and Transporting Objects
Assignment
Week05 (Oct. 2, 5)
Concepts and ideas
- Introduction
- Appending Data to a Vector
- Inserting Data into a Vector
- Understanding the Recycling Rule
- Creating a Factor (Categorical Variable)
- Combining Multiple Vectors into One Vector and a Factor
- Creating a List
- Selecting List Elements by Position
- Selecting List Elements by Name
- Building a Name/Value Association List
- Removing an Element from a List
- Flatten a List into a Vector
- Removing NULL Elements from a List
- Removing List Elements Using a Condition
- Initializing a Matrix
- Performing Matrix Operations
- Giving Descriptive Names to the Rows and Columns of a Matrix
- Selecting One Row or Column from a Matrix
- Initializing a Data Frame from Column Data
- Initializing a Data Frame from Row Data
- Appending Rows to a Data Frame
- Preallocating a Data Frame
- Selecting Data Frame Columns by Position
- Selecting Data Frame Columns by Name
- Selecting Rows and Columns More Easily
- Changing the Names of Data Frame Columns
- Editing a Data Frame
- Removing NAs from a Data Frame
- Excluding Columns by Name
- Combining Two Data Frames
- Merging Data Frames by Common Column
- Accessing Data Frame Contents More Easily
- Converting One Atomic Value into Another
- Converting One Structured Data Type into Another
Assignment
Week06 (Oct. 9, 12)
Concepts and ideas
- Introduction
- Splitting a Vector into Groups
- Applying a Function to Each List Element
- Applying a Function to Every Row
- Applying a Function to Every Column
- Applying a Function to Groups of Data
- Applying a Function to Groups of Rows
- Applying a Function to Parallel Vectors or Lists
Strings and Dates
Announcement
- First quiz on Week 07, Tuesday class (Oct. 16)
- RANGE: Week 01 - 03 materials + lecture content + textbook
- Textbook:
- chapter 2, 3, 4, 5
- NEXT quiz will be held on Oct. 23 during the mid term schedule.
- The 2nd quiz will cover 1st quiz + Week 05-07 materials.
Assignment
Week07 (Oct. 16, 19)
Concepts and ideas
- Introduction
- Counting the Number of Combinations
- Generating Combinations
- Generating Random Numbers
- Generating Reproducible Random Numbers
- Generating a Random Sample
- Generating Random Sequences
- Randomly Permuting a Vector
- Calculating Probabilities for Discrete Distributions
- Calculating Probabilities for Continuous Distributions
- Converting Probabilities to Quantiles
- Plotting a Density Function
Assignment
개인과제
Week08 (Oct. 23, 26)
Mid-term period
Range:
- textbook Ch 6, 8, 9
- week 01-07 materials
Week09 (Oct. 30, Nov. 2)
Concepts and ideas
General Statistics
t-test
ANOVA
Factorial ANOVA
repeated measure anova
correlation and regression and multiple regression
- Before regression, SS actually is sum of (error squared of guessing estimates).
- sum of error square = 오차의 제곱의 합 = SS (오차라는 단어 없이 사용되는 용어)
- For this, read carefully 표준오차 잔여변량 (standard error residual) in Regression document.
- Introduction
- Summarizing Your Data
- Calculating Relative Frequencies
- Tabulating Factors and Creating Contingency Tables
- Testing Categorical Variables for Independence
- Calculating Quantiles (and Quartiles) of a Dataset
- Inverting a Quantile
- Converting Data to Z-Scores
- Testing the Mean of a Sample (t Test)
- Forming a Confidence Interval for a Mean
- Forming a Confidence Interval for a Median
- Testing a Sample Proportion
- Forming a Confidence Interval for a Proportion
- Testing for Normality
- Testing for Runs
- Comparing the Means of Two Samples
- Comparing the Locations of Two Samples Nonparametrically
- Testing a Correlation for Significance
- Testing Groups for Equal Proportions
- Performing Pairwise Comparisons Between Group Means
- Testing Two Samples for the Same Distribution
Assignment
Week10 (Nov. 6, 9)
Assignment
Week11 (Nov. 13, 16)
Concepts and ideas
getting started
basics
navigating in r
input output in r
data structures
data transformations
- Introduction
- Creating a Scatter Plot
- Adding a Title and Labels
- Adding a Grid
- Creating a Scatter Plot of Multiple Groups
- Adding a Legend
- Plotting the Regression Line of a Scatter Plot
- Plotting All Variables Against All Other Variables
- Creating One Scatter Plot for Each Factor Level
- Creating a Bar Chart
- Adding Confidence Intervals to a Bar Chart
- Coloring a Bar Chart
- Plotting a Line from x and y Points
- Changing the Type, Width, or Color of a Line
- Plotting Multiple Datasets
- Adding Vertical or Horizontal Lines
- Creating a Box Plot
- Creating One Box Plot for Each Factor Level
- Creating a Histogram
- Adding a Density Estimate to a Histogram
- Creating a Discrete Histogram
- Creating a Normal Quantile-Quantile (Q-Q) Plot
- Creating Other Quantile-Quantile Plots
- Plotting a Variable in Multiple Colors
- Graphing a Function
- Pausing Between Plots
- Displaying Several Figures on One Page
- Opening Additional Graphics Windows
- Writing Your Plot to a File
- Changing Graphical Parameters
Assignment
Week12 (Nov. 20, 23)
Announcement
Quiz 03: Nov. 23
Concepts and ideas
chi-square test
probability
general statistics
Graphics
Assignment
Week13 (Nov. 27, 30)
Concepts and ideas
Do the following
S1 <- c(89, 85, 85, 86, 88, 89, 86, 82, 96, 85, 93, 91,
98, 87, 94, 77, 87, 98, 85, 89, 95, 85, 93, 93,
97, 71, 97, 93, 75, 68, 98, 95, 79, 94, 98, 95)
S2 <- c(60, 98, 94, 95, 99, 97, 100, 73, 93, 91, 98,
86, 66, 83, 77, 97, 91, 93, 71, 91, 95, 100,
72, 96, 91, 76, 100, 97, 99, 95, 97, 77, 94,
99, 88, 100, 94, 93, 86)
S3 <- c(95, 86, 90, 90, 75, 83, 96, 85, 83, 84, 81, 98,
77, 94, 84, 89, 93, 99, 91, 77, 95, 90, 91, 87,
85, 76, 99, 99, 97, 97, 97, 77, 93, 96, 90, 87,
97, 88)
S4 <- c(67, 93, 63, 83, 87, 97, 96, 92, 93, 96, 87, 90,
94, 90, 82, 91, 85, 93, 83, 90, 87, 99, 94, 88,
90, 72, 81, 93, 93, 94, 97, 89, 96, 95, 82, 97)
scores <- list(S1=S1,S2=S2,S3=S3,S4=S4)
- find means for each element in “scores” in a list format
- find standard deviation for each element in “scores” in a data frame format
- find variance for each element in “scores” in a data frame format without using “var” function
longdata<- c(-1.850152, -1.406571, -1.0104817, -3.7170704,
-0.2804896, 0.9496313, 1.346517, -0.1580926, 1.6272786,
-2.4483321, -0.5407272, -1.708678, -0.3480616, -0.2757667,
-1.2177024)
- make “longdata” to a matrix whose size is 3 by 5
- name columns “trial1, trial2, . . . . trial5”
- name rows “subject1, subject2, subject3”
- get means for each subject
- attach the above data to the matrix data and name it “longtemp.”
- get standard deviation for each trial
- attach the above data to the matrix data, “longtemp.”
suburbs <- read.csv("http://commres.net/wiki/_export/code/r/data_transformations?codeblock=15", head=T, sep=" ")
- get subrubs data as the above
- get population means by each state (listed in the data, suburbs)
- use aggregate and refer to the below e.g.
attach(Cars93) aggregate(MPG.city ~ Origin, Cars93, mean)
- get population sum by each county with tapply function.
- tapply(number, byfactor, function)
- how many counties are there?
- Use Cars93 data, get MPG.city mean by Origin.
Using pnorm, qnorm
pnorm : get proportion out of normal distribution whose characteristics are mean and sd
pnorm(84, mean=72, sd=15.2, lower.tail=FALSE)
- What is the value of the below?
pnorm(1)
- How would you get 68, 95, 99% from pnorm
- use ?pnorm and see the default option
- generate 10 random numbers with runif function
year <- c(1900:2016) # years in vector year world.series <- data.frame(year)
- get 10 year samples out of world.series data with “sample” command
- how would you get the sample sample again latter?
pnorm(110, mean=100, sd=10)
- What would be the result from the above?
library(MASS) # load the MASS package tbl = table(survey$Smoke, survey$Exer) tbl # the contingency table
summary(tbl)
- read the above output and interpret
- what about the below one?
chisq.test(tbl)
see first chi-square test
see chi-square test in r document space for more
library(MASS) cardata <- data.frame(Cars93$Origin, Cars93$Type) cardata
- Can you say the types of cars are different by the Origins?
dur <- faithful$eruptions dur
- make the above data into z-score (zdur).
- get mean of the zdur
- get sd of the zdur
set.seed(1123) x <- rnorm(50, mean=100, sd=15)
- test x against population mean 95.
- test x against population mean 99.
- are they different from each other?
- what would you do if you want to see the different result from the second one?
a = c(65, 78, 88, 55, 48, 95, 66, 57, 79, 81)
> t.test(a, mu=60)
One Sample t-test
data: a
t = 2.3079, df = 9, p-value = 0.0464
alternative hypothesis: true mean is not equal to 60
95 percent confidence interval:
60.22187 82.17813
sample estimates:
mean of x
71.2
- find the t critical value with function qt.
- explain what happens in the next code
- read (or remind) what pnorm and qnorm do.
> s <- sd(x) > m <- mean(x) > n <- length(x) > n [1] 50 > m [1] 96.00386 > s [1] 17.38321 > SE <- s / sqrt(n) > SE [1] 2.458358 > E <- qt(.975, df=n-1)*SE > E [1] 4.940254 > m + c(-E, E) [1] 91.0636 100.9441 >
- what's wrong with the below?
t.test(x)
> mtcars
- using aggregate, get mean for each trnas. type.
- compare the difference of mileage between auto and manual cars.
- use t.test (two sample)
- “use var.equal=T” option
a = c(175, 168, 168, 190, 156, 181, 182, 175, 174, 179) b = c(185, 169, 173, 173, 188, 186, 175, 174, 179, 180)
- stack them into data c
- convert colnames into score and trans
- t.test score by trans with var.equal option true.
- aov test
- see t.test t value, t = -0.9474 and F value, F = ?
Assignment
- Do Ex 1 part in linear regression
Week14 (Dec. 4, 7)
Concepts and ideas
ANOVA
oneway anova
twoway anova
linear regression
multiple regression
partial and semipartial correlation
statistical regression methods
sequential_regression
Linear Regression and ANOVA
http://commres.net/wiki/text_mining_example_with_korean_songs
Assignment
Week15 (Dec. 11, 14)
Final quiz
Part I (필기시험): NO open book.
- factor analysis - 이론적인 이해와 관련된 부분
- r 과 관련된 내용 중 통계에 대한 이해와 관련된 부분, 예를 들면
- t-test, ANOVA, Factorial ANOVA output에 대한 이해
- regression, multiple regression output에 대한 이해 등
Part II (r 실기시험): 교재와 R help만 허용
Week16 (Dec. 18, 21)
Final-term